

DataCells can be merged together to display a common value, this results into a SpannedCell. These cells can span horizontally, vertically, or both. Cells will span automatically when adjacent values are equal.
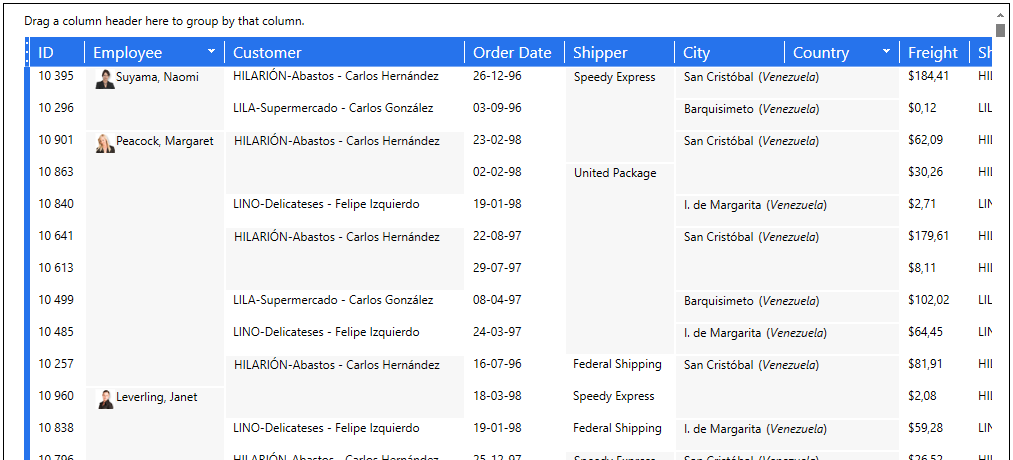
Figure 1: Example of a grid using both horizontal and vertical Spanned Cells
The TableView.AllowCellSpanning property must be set to true to activate cell spanning.
The Column.CellSpanningDirection is used to set how particular cells span. In order to span cells vertically, the corresponding columns must be set to CellSpanningDirection.Row. To have cells span horizontally, the corresponding columns must be set to CellSpanningDirecton.Column. Cells can span in both direction by setting the Column.CellSpanningDirection property to CellSpanningDirection.Both.
A spanning cell can be customized in different ways. First, to change its appearance, you can provide an implicit style on SpannedCell (see example 1).
Second, a configuration can be furnished. Use the DataGridControl.SpannedCellConfigurationSelector property to provide a SpannedCellConfiguration, on which you can set the following properties: ContentTemplate, ContentTemplateSelector, ContentStringFormat, HorizontalContentAlignement, and VerticalContentAlignement (see example 2).
Third, cells can be set to span on criteria other then being of equal value. In order to customize how cells span, use the DataGridControl.SpannedCellSelector property to provide a SpannedCellSelector. Then override its CanMerge method to provide the rules used to determine if two SpannedCellFragments can be merged to create a SpannedCell, and override its SelectContent method to provide the rules used to determine the content displayed in the SpannedCell (see example 3).
All examples in this topic assume that the grid is bound to the Orders table of the Northwind database, unless stated otherwise.
Example 1: Styling Spanned Cells
The following example demonstrates how to change the background and set a border around spanned cells through a style.
| XAML |
Copy Code |
|---|---|
<Grid xmlns:xcdg="http://schemas.xceed.com/wpf/xaml/datagrid"> <Grid.Resources> <xcdg:DataGridCollectionViewSource x:Key="cvs_orders" Source="{Binding Source={x:Static Application.Current}, Path=Orders}" /> <Style x:Key="spannedCellBorderStyle" TargetType="{x:Type Border}"> <Setter Property="Background" Value="LightBlue" /> <Setter Property="BorderBrush" Value="DarkBlue" /> <Setter Property="BorderThickness" Value="1" /> </Style> <Style TargetType="{x:Type xcdg:SpannedCell}"> <Setter Property="CellContainerStyle" Value="{StaticResource spannedCellBorderStyle}" /> </Style> </Grid.Resources> <xcdg:DataGridControl ItemsSource="{Binding Source={StaticResource cvs_orders}}"> <xcdg:DataGridControl.View> <xcdg:TableView AllowCellSpanning="True" /> </xcdg:DataGridControl.View> <xcdg:DataGridControl.Columns> <xcdg:Column FieldName="ShipCountry" CellSpanningDirection="Row" /> </xcdg:DataGridControl.Columns> </xcdg:DataGridControl> </Grid> | |
Example 2: Configuring Spanned Cells
The following example demonstrates how to center vertical and horizontal content alignment through a SpannedCellConfigurationSelector.
| XAML |
Copy Code |
|---|---|
<Grid xmlns:xcdg="http://schemas.xceed.com/wpf/xaml/datagrid"> <Grid.Resources> <xcdg:DataGridCollectionViewSource x:Key="cvs_orders" Source="{Binding Source={x:Static Application.Current}, Path=Orders}" /> <xcdg:CustomSpannedCellConfigurationSelector x:Key="configurationSelector" /> </Grid.Resources> <xcdg:DataGridControl ItemsSource="{Binding Source={StaticResource cvs_orders}}" SpannedCellSelector="{StaticResource configurationSelector}"> <xcdg:DataGridControl.View> <xcdg:TableView AllowCellSpanning="True" /> </xcdg:DataGridControl.View> <xcdg:DataGridControl.Columns> <xcdg:Column FieldName="ShipCountry" CellSpanningDirection="Row" /> </xcdg:DataGridControl.Columns> </xcdg:DataGridControl> </Grid> | |
| C# |
Copy Code |
|---|---|
public sealed class CustomSpannedCellConfigurationSelector : SpannedCellConfigurationSelector { public override ISpannedCellConfiguration SelectConfiguration(object content, IEnumerable<SpannedCellFragment> fragments) { return new SpannedCellConfiguration() { HorizontalContentAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center, VerticalContentAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Center }; } } | |
Example 3: Creating a Custom Spanning
The following example demonstrates how to span cells across a range of values.
| XAML |
Copy Code |
|---|---|
<Grid xmlns:xcdg="http://schemas.xceed.com/wpf/xaml/datagrid"> <Grid.Resources> <xcdg:DataGridCollectionViewSource x:Key="cvs_orders" Source="{Binding Source={x:Static Application.Current}, Path=Orders}" /> <local:CustomSpannedCellSelector x:Key="spannedCellSelector" /> </Grid.Resources> <xcdg:DataGridControl ItemsSource="{Binding Source={StaticResource cvs_orders}}" SpannedCellSelector="{StaticResource spannedCellSelector}"> <xcdg:DataGridControl.View> <xcdg:TableView AllowCellSpanning="True" /> </xcdg:DataGridControl.View> <xcdg:DataGridControl.Columns> <xcdg:Column FieldName="Freight" CellSpanningDirection="Row" /> </xcdg:DataGridControl.Columns> </xcdg:DataGridControl> </Grid> | |
| C# |
Copy Code |
|---|---|
public sealed class CustomSpannedCellSelector : SpannedCellSelector { private const decimal Range = 10m; public override bool CanMerge(SpannedCellFragment x, SpannedCellFragment y) { if ((x.Column == y.Column) && (x.Column.FieldName == "Freight")) { var xBound = this.GetLowerBound(x); var yBound = this.GetLowerBound(y); return xBound.HasValue && yBound.HasValue && (xBound.Value == yBound.Value); } return false; } public override object SelectContent(IEnumerable<SpannedCellFragment> fragments) { var first = fragments.FirstOrDefault(); var bound = (first != null) ? this.GetLowerBound(first) : null; if (!bound.HasValue) return null; return string.Format("{0} - {1}", bound.Value, bound.Value + Range); } private decimal? GetLowerBound(SpannedCellFragment x) { var content = x.Content; if (!(content is decimal)) return null; var value = (decimal)content; return Math.Floor(value / Range) * Range; } } | |